The ICT Opening Range is a crucial concept in Inner Circle Trading (ICT), focusing on the first 30 to 60 minutes after the market opens. During this period, traders analyze the price action to assess the market’s direction, liquidity, and potential trading opportunities. By understanding the opening range, traders can establish a clearer market bias, leading to more precise trading decisions.
What is the ICT Opening Range?
The ICT Opening Range focuses on the price action that happens in the first 30 to 60 minutes after a major market opens. It is the initial price range formed by the high and low of the first 30 minutes of trading, and it provides a clear view of market sentiment right from the start.
The idea is simple: track how the market behaves when it first opens, and use that information to predict the market’s direction. By closely watching the price action during the first few minutes, we can get a sense of whether the bulls or bears are in control.

Focus on Volume Analysis Between 8:00 AM and 9:30 AM (New York Local Time)
The highest volume of the day typically occurs between 8:00 AM and 9:00 AM (New York Local Time). This period is critical as it often sets the high or low of the day. The opening range between 8:00 AM and 9:00 AM can help identify key market levels, such as liquidity pools and possible stop runs, which are important for predicting price movement during the day
Why Does It Matter?
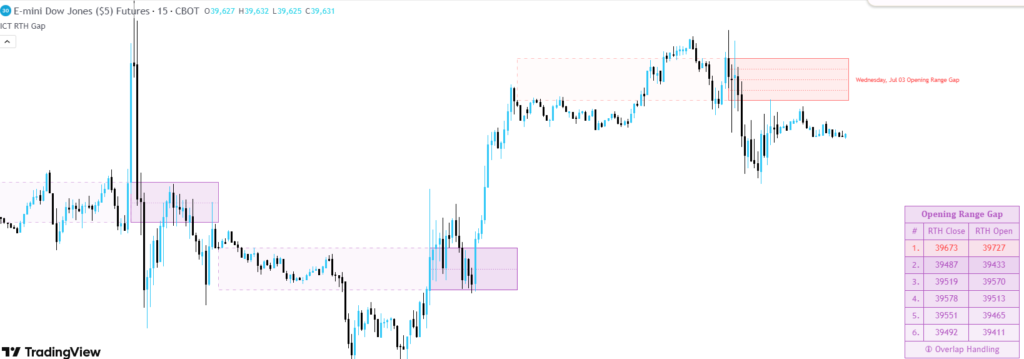
This range acts as a reference point for market direction and liquidity. The gap created acts as price magnet and attract the price. As shown in the below image.

- Direction: The opening range helps us understand whether the market is more likely to go up or down after the bell rings.
- Key Levels: It reveals important levels of support and resistance—essential information for setting up trades.
- Market Sentiment: The first 30 minutes can indicate the market’s mood (bullish or bearish), helping us gauge the overall tone of the day.
iCT opening range gap strategy
- Wait for the First 30 Minutes
When the market opens, don’t rush into trades immediately. Wait for the first 30 minutes to see where the market is headed. Observe price action carefully. Is the price consistently making higher highs (bullish) or lower lows (bearish)? Or is it choppy, indicating indecision? - Identify the High and Low of the Range
Once the 30-minute window has passed, mark the high and low of the range. These two levels will act as key reference points for the rest of the session. If the market breaks above the high, it could signal a bullish move, and if it breaks below the low, expect a bearish move. - Look for Confirmations
After defining the opening range, look for confirmation through other technical indicators like moving averages, RSI, or candlestick patterns. If the market is above the opening range high and showing strong bullish signals, you might consider taking a long trade. If it’s below the opening range low and showing signs of weakness, shorting could be the way to go. - Monitor Liquidity and Volume
Pay attention to volume during this opening phase. High volume can confirm a breakout in the direction of the range, while low volume could indicate a fakeout or a lack of conviction in the move.
Why is the opening range from 9:30 to 10:00 AM important?
Analyzing the opening range helps traders understand how the market is behaving early on, whether it’s showing signs of strength (bullish) or weakness (bearish), and gives clues about possible price movements
What is the ICT Opening Range time?
he ICT Opening Range time typically refers to the first 30 to 60 minutes after the market opens, often from 9:30 AM to 10:00 AM (New York Local Time). During this time, traders analyze price action to identify market direction, liquidity levels, and potential trading opportunities.
What is the opening range breakout in ICT?
Opening range gap breakout suggest that market is shift its sentiment and a possible reversal is take place. For future price action market will retest the gap area and give a chance to execute trades.


