An Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG) represents a failed Fair Value Gap (FVG). When price revisits a Fair Value Gap but fails to respect it as support or resistance, the FVG converts into an IFVG. This transformed price structure subsequently serves as an institutional reference point on charts.
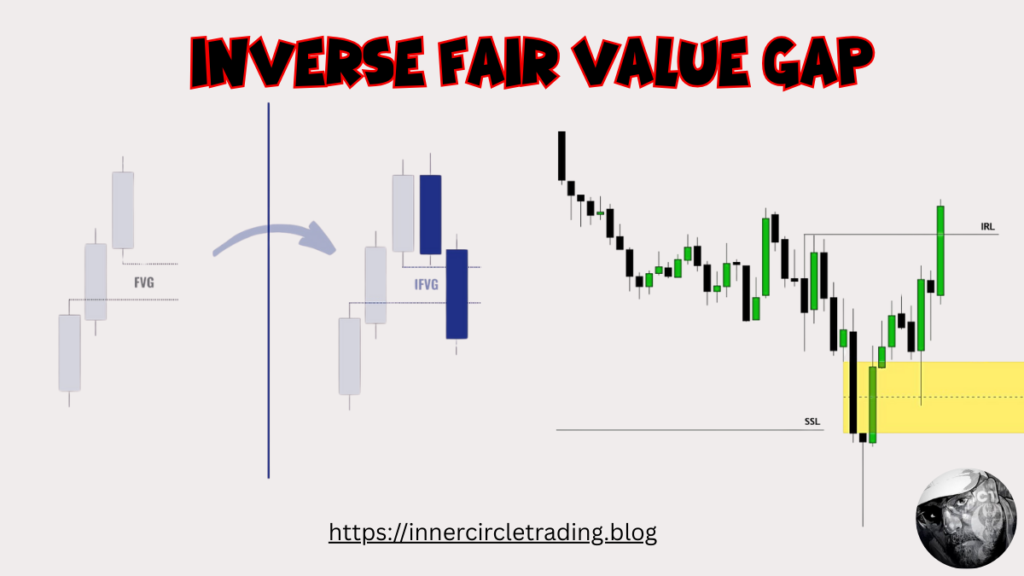
IFVGs function as significant reversal patterns, signaling a momentum shift from bullish to bearish or vice versa. Traders use these structures to identify potential turning points where market sentiment has changed direction.
What does an inverse fair value gap mean?
An Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG) forms when a previously established Fair Value Gap gets violated and filled by price action. Essentially, it represents a situation where the market has returned to and moved through an area that was previously bypassed during a strong move.
While a traditional FVG indicates an imbalance between buyers and sellers that creates a price void, an IFVG suggests that this imbalance has been neutralized, potentially creating a new trading opportunity in the opposite direction.
How does IFVG form?
IFVGs form through a specific sequence of price action:
- First, a traditional Fair Value Gap forms when price makes a sharp move, creating a gap in the chart
- Later, when price returns to the FVG area and moves completely through it (violating the gap), an IFVG is created
- A Bullish FVG can be converted into a Bearish IFVG when the price moves downward through it
- Similarly, a Bearish FVG can be converted into a Bullish IFVG when the price moves upward through it
This violation of the original FVG often signals a potential shift in market sentiment or direction, making IFVGs valuable for identifying possible reversal points.
What are the Basic Types of IFVG?
ICT Inverse Fair Value Gap has basically two types.
What is a Bullish Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG)?
A Bullish Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG) happens when a Bearish Fair Value Gap (FVG) doesn’t work the way traders expect. Normally, in a bearish FVG, the price should go down. But sometimes, the price doesn’t fall — instead, it goes up from that area.
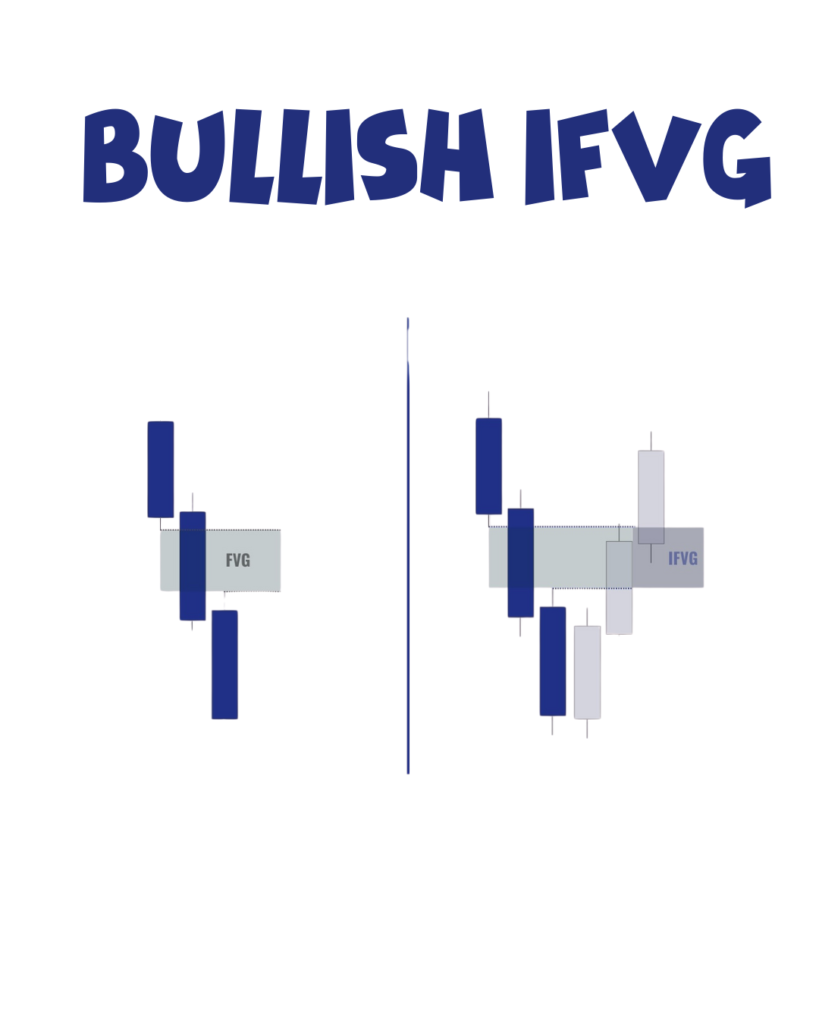
When this happens, that same gap area can turn into support. In the future, when the price comes back to that zone, it often bounces up again. This shows that smart money is interested in that area. So, traders may use this spot to enter long (buy) trades, expecting the price to move higher from there.
What is a Bearish Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG)?
A Bearish Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG) occurs when a Bullish Fair Value Gap (FVG) fails to function as expected. In traditional market theory, a bullish FVG typically signals an area where the price should rise. However, when a bearish IFVG forms, the price unexpectedly declines from this region instead of advancing.

This failed bullish area undergoes a significant transformation – what was originally anticipated to act as support now converts into resistance. When price later returns to this zone, it often rejects downward again, indicating persistent selling pressure. Traders frequently utilize these bearish IFVG zones as strategic entry points for short positions, anticipating continued downward price movement.
What is the Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG) trading strategy?
Trading IFVGs effectively involves a systematic approach:
- Identify non-respected FVGs: Look for Fair Value Gaps that price has returned to and violated, especially those in ICT “Kill Zones” (London/New York sessions, high-volume trading periods)
- Wait for price to retest: After an IFVG forms, wait for price to return to this area again, which often serves as support/resistance
- Confirm with additional factors: Look for confluence with other technical elements, like:
- Key support/resistance levels
- Order blocks
- Liquidity zones
- Market structure breaks
- Manage risk appropriately: Place stop losses beyond the IFVG zone to give the trade room to breathe
- Set realistic targets: Consider taking profits at the next significant support/resistance level or using a risk-reward ratio of at least 1:2
What is the difference between a Fair Value Gap (FVG) and an Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG)?
A Fair Value Gap (FVG) is an imbalance in price that the market often returns to fill. An Inverse Fair Value Gap (IFVG) forms when the original FVG fails — instead of respecting the expected direction, price moves the opposite way, turning that zone into a future support or resistance level.
How does an IFVG act as support or resistance?
If a bearish FVG fails, it can become a bullish IFVG, acting as a support zone where the price bounces up. If a bullish FVG fails, it becomes a bearish IFVG, acting as a resistance zone where the price may drop.
Are IFVGs more reliable than regular FVGs?
Not necessarily. IFVGs simply offer a different perspective — they highlight what happens when the market doesn’t respect the expected FVG behavior. They’re useful for spotting traps, liquidity shifts, and reversal zones, especially when combined with smart money concepts.
What if the price doesn’t respect the FVG during kill zones?
If price breaks through the FVG with momentum during a Kill Zone, that’s a sign of a possible break of structure. Be flexible — the failed IFVG might flip into an inverse one, giving you a new trade setup in the opposite direction.


