ICT Smart Money Technique (SMT) Divergence is a powerful concept that reveals discrepancies between correlated assets, signaling potential turning points in financial markets. By mastering SMT divergence, traders can identify and use price manipulation to their advantage.
This blog post will cover everything you need to know about ICT SMT divergence.
What is ICT SMT Divergence?
SMT Divergence occurs when two correlated assets, observed within the same timeframe, exhibit opposing price structures. Under normal conditions, positively correlated assets, like EUR/USD and GBP/USD, move in the same direction. However, divergence happens when one asset makes a higher high, while the other fails to do so, or vice versa.
This discrepancy indicates potential manipulation by institutional traders and suggests a market reversal. SMT divergence is not limited to positively correlated assets; it can also occur in negatively correlated pairs, such as EUR/USD and the US Dollar Index (DXY), where they typically move in opposite directions.
How to Trade SMT Divergence
SMT divergence serves as a primary signal for reversal in correlated assets. To effectively trade SMT divergence:
Identify Divergence: Look for discrepancies in price action between two correlated assets. For positively correlated pairs, watch for one asset making a higher high while the other fails to do so. For negatively correlated pairs, observe one making a lower high while the other fails to make a lower low.
Analyze the PD Array Matrix: Use ICT tools like the PD Array (order blocks, fair value gaps, and breaker blocks) to confirm potential reversal zones. For example:
- If EUR/USD is bullish and forming higher highs, while GBP/USD forms a lower high, it signals potential bearish divergence. When EUR/USD reaches a bearish PD array, such as an order block, the price is likely to reverse.
Enter Trades: Once divergence is spotted and aligned with a PD array, execute your trade with proper risk management.
Bullish ICT SMT Divergence
In Bullish SMT Divergence, discrepancies between positively correlated assets signal a potential upward shift in the market.
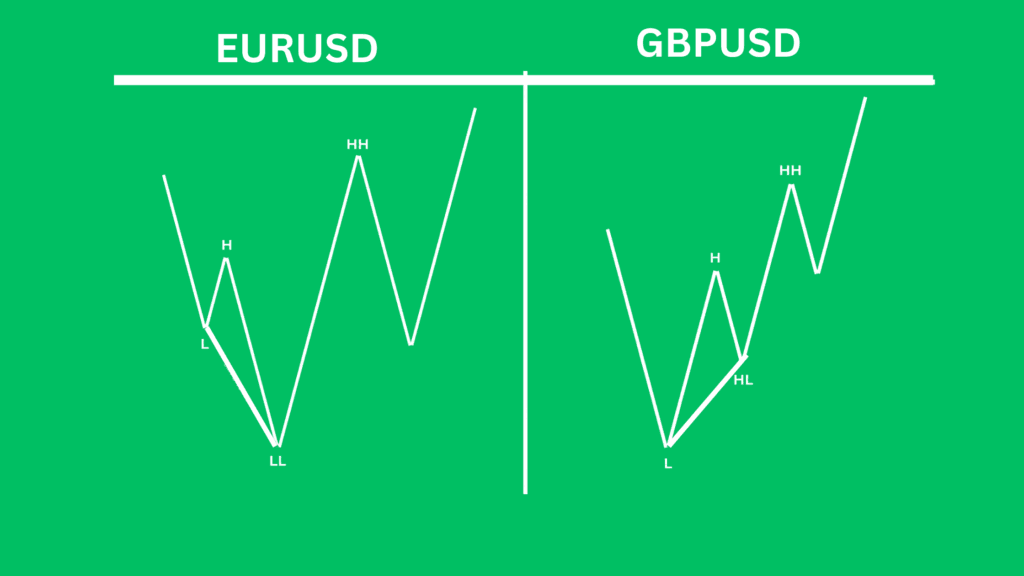
Comparison of Lows: Look at the lows of two positively correlated assets, such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD, at their key Premium and Discount Arrays (PD Arrays Matrix).
If one asset fails to make a lower low while the other achieves it, this indicates bullish SMT divergence.
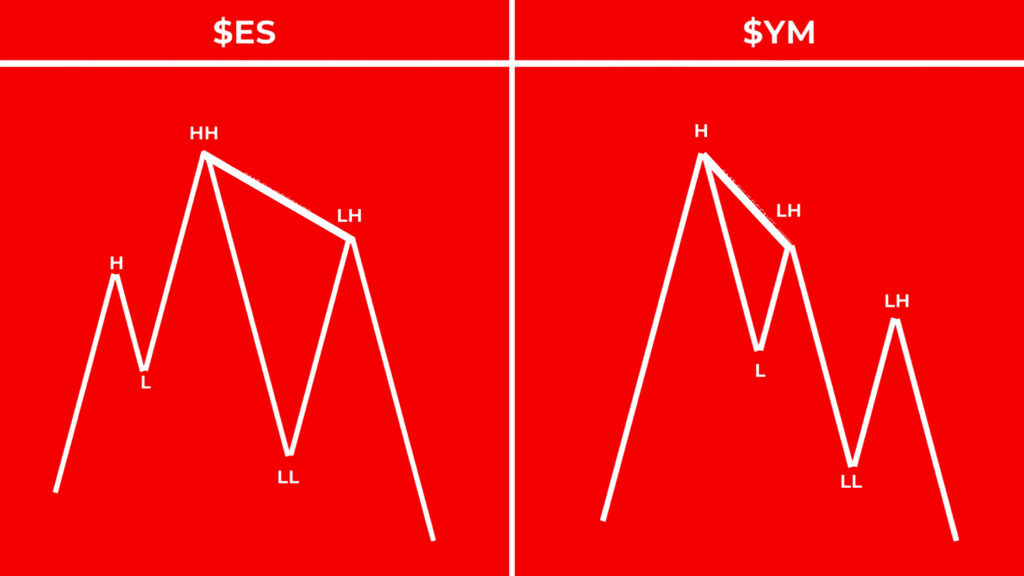
Bearish ICT SMT Divergence
Bearish SMT Divergence occurs when two positively correlated assets exhibit discrepancies in their price action near significant bearish Premium and Discount Arrays (PD Arrays). This signals a potential short-term market shift toward a decline.
Download SMT Divergence Notes PDF
By Clicking on the download button you can download notes of Smart money Technique Divergence in PDF format
What are some Popular Pairs for finding SMT divergence
Forex: EUR/USD vs. GBP/USD
Indices: NQ (Nasdaq 100) vs. ES (S&P 500)
Metals: XAU/USD vs. XAG/USD
Crypto: BTC vs. ETH
What are the different types of SMT divergence?
There are two main types of SMT divergence: Bullish and Bearish divergence.
Bullish SMT: This happens when two positively correlated assets are moving lower, but one asset makes a higher low, while the other makes a lower low.
Bearish SMT: This occurs when two positively correlated assets are moving higher, but one asset makes a lower high, while the other makes a higher high.
Why does SMT divergence happen?
SMT divergence happens because large institutional traders (smart money) manipulate the market. They create a situation where two normally correlated assets move differently. For example, one asset may make a higher high or lower low, while the other doesn’t. This is done to trap retail traders and mislead them into thinking the trend will continue. In reality, it often signals a market reversal, as smart money is setting up a move in the opposite direction to collect liquidity and profit from the shift.