Welcome to Inner Circle Trader
Master the art of trading with Michael J. Huddleston, also known as Inner Circle Trader (ICT), the creator of the Smart Money Concept,Order Blocks, Fair Value Gaps. As a pioneer in trading education, Michael simplifies complex strategies into actionable insights, empowering traders to achieve consistent success. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned professional, his proven methods provide the tools you need to excel. Elevate your trading journey with Inner Circle Trader today and unlock your full potential.

Latest Blogs
Master Advanced ICT Trading Concepts and Trade with Precision
Our Team
View All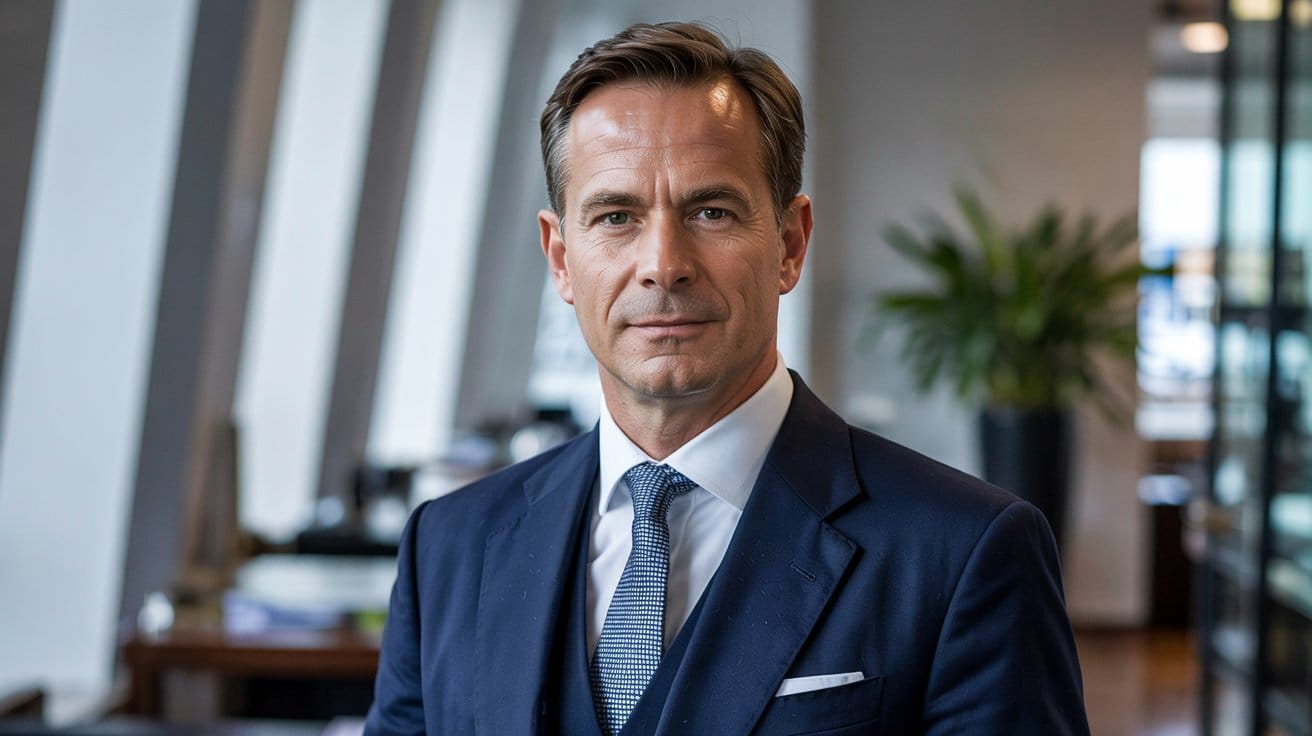
Michael Huddleston
Founder of ICT Tradings & Trade Track
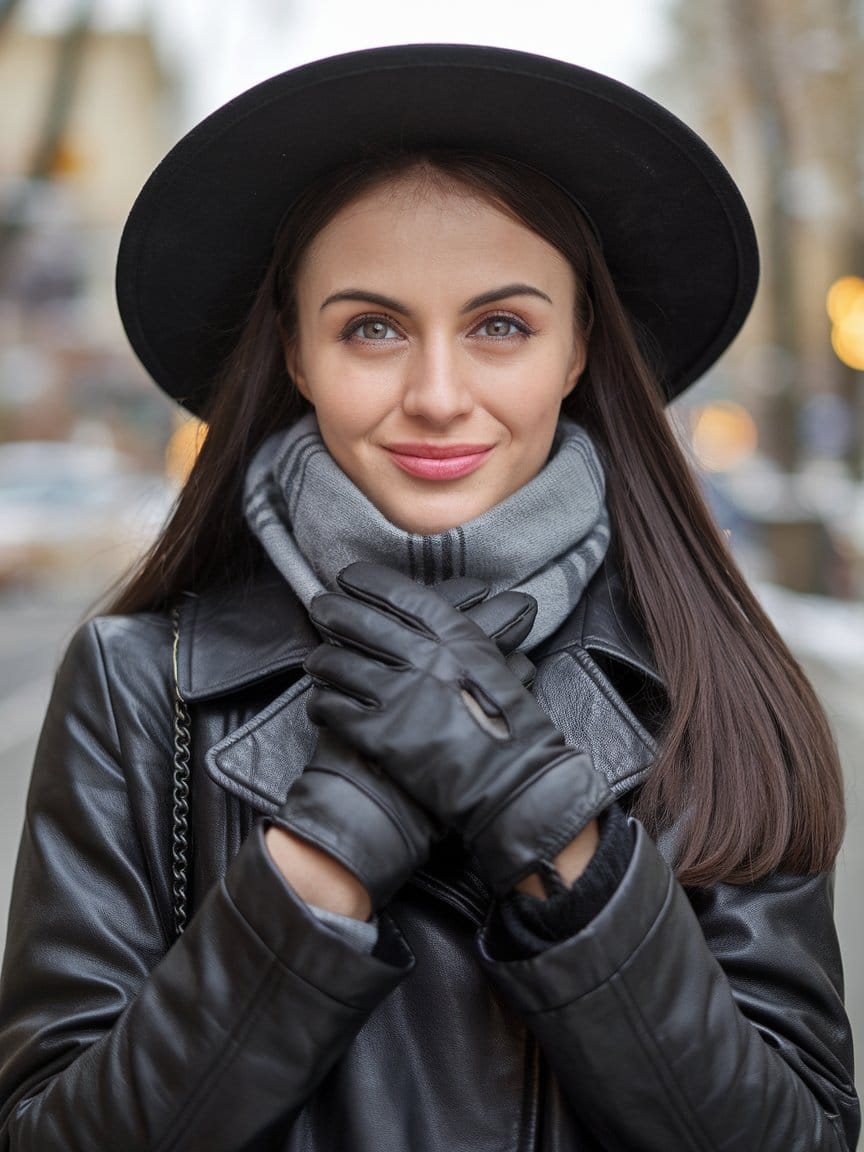

Julia
Co-Founder of ICT Tradings
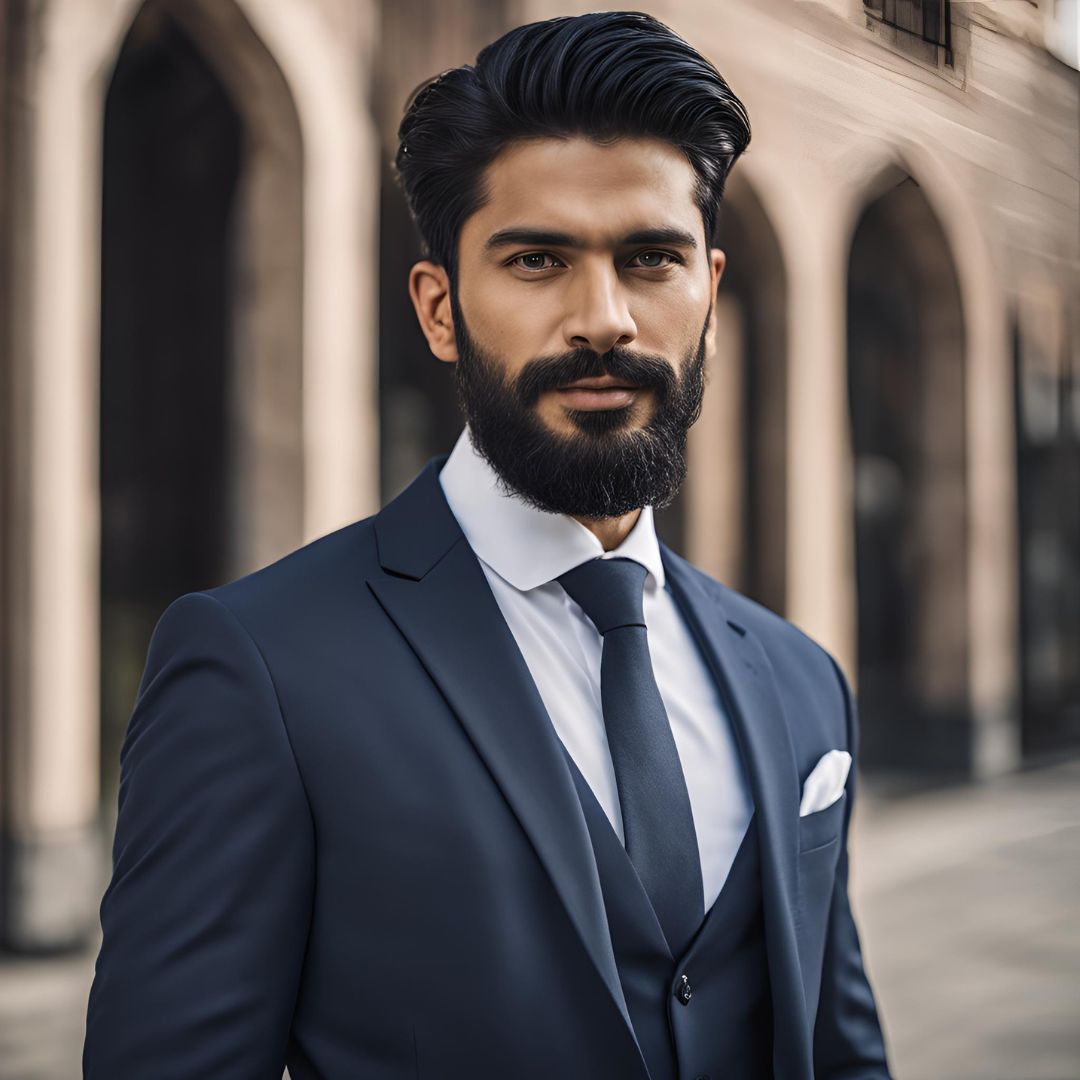

Rohan
Research Head of ICT Tradings
Get Inner Circle Trader (ICT) Book PDF
I’m excited to share my free eBook with you! It’s filled with easy-to-understand tips and strategies to help you succeed in trading.
Grab your copy of the ICT Michael Huddleston book today and take the first step toward mastering trading. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide is your ultimate resource for success in the markets!