Master ICT Scalping Strategy for Fast Trades

The ICT Scalping Strategy is a highly effective method for traders looking to capitalize on short-term market movements. Developed within the framework of Inner Circle Trading (ICT), this strategy focuses on capturing small price changes by making numerous trades throughout the day. If you’re aiming for fast profits with minimal time exposure, then the ICT scalping method is a perfect approach to consider. In this guide, we’ll break down the essential principles and provide a step-by-step guide on how to implement this powerful trading strategy effectively.
Introduction to ICT Scalping Strategy
Scalping is one of the most popular trading styles in the forex market, and when combined with the techniques of Inner Circle Trading (ICT), it becomes an even more powerful tool. The ICT Scalping Strategy is built around the idea of making fast trades based on small price fluctuations, usually within a few minutes or hours. This approach is particularly appealing to day traders who prefer to avoid holding positions overnight and are comfortable with high-frequency trading.
Scalping is not about waiting for large market shifts; instead, it’s about identifying small, consistent movements and profiting from them. With ICT, the key focus lies on market structure, liquidity pools, and Kill Zones, which offer traders a precise framework for timing entries and exits.
The importance of the ICT scalping strategy lies in its ability to make the most of volatile conditions. By using ICT’s concepts of liquidity zones and order blocks, scalpers can enhance their success rates in finding profitable trades. This strategy requires a deep understanding of market dynamics and sharp execution due to the rapid nature of scalping trades.
Core Principles of the ICT Scalping Strategy
Understanding the Market Structure
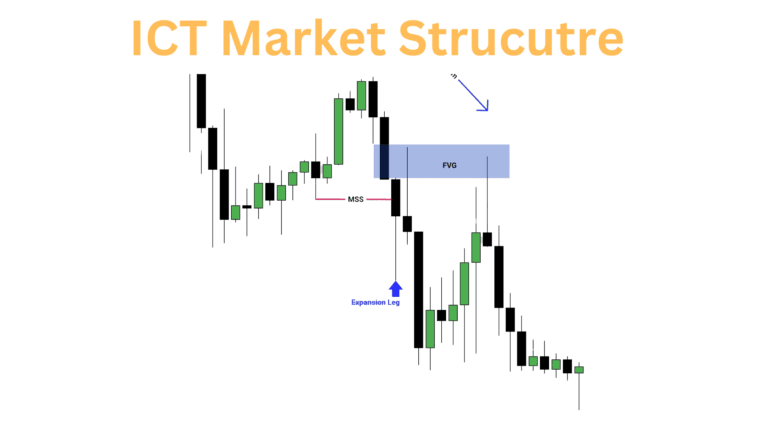
One of the fundamental principles of the ICT Scalping Strategy is the recognition and understanding of market structure. ICT focuses heavily on identifying key market zones, such as premium and discount levels, which allow traders to determine the optimal times for entering and exiting trades. These levels are determined by analyzing the overall trend direction and the movement of liquidity within the market.
A solid understanding of market structure is essential for scalping because it helps traders identify areas where price reversals are likely to occur. This allows scalpers to enter trades just before the price moves in their favor, making it easier to profit from short-term movements
Liquidity Pools and Order Blocks
In ICT, the concepts of liquidity pools and order blocks play a critical role in scalping strategies. Liquidity pools are areas in the market where large volumes of buy or sell orders are placed. These pools often act as magnets for price movement, making them ideal spots for traders to enter and exit positions quickly. Scalpers using the ICT strategy aim to take advantage of these liquidity zones by placing trades as the price moves into these areas.
On the other hand, order blocks refer to zones where large institutional orders are likely to be placed. Recognizing these zones can give scalpers an edge in determining potential reversals or price consolidation points, allowing for better trade precision.
Using Time Frames in ICT Scalping
For scalpers, choosing the right time frame is crucial. The ICT Scalping Strategy typically utilizes short-term time frames such as the 1-minute or 5-minute charts. These time frames allow traders to catch quick market movements while ensuring that they stay within the limits of short-term trading. This contrasts with longer-term strategies that may involve holding trades for several hours or even days.
By focusing on these shorter time frames, ICT scalpers can react quickly to market changes and make multiple trades throughout a single trading session. This makes scalping an ideal strategy for traders who thrive in fast-paced environments.
Tools and Indicators for ICT Scalping
To effectively use the ICT Scalping Strategy, having the right tools and indicators is essential. These tools not only help you identify profitable trade setups but also provide clarity on when to enter and exit trades. The ICT framework emphasizes precision and discipline, and by leveraging the right indicators, you can significantly enhance your scalping performance.
ICT Premium/Discount Tool
One of the most useful tools in ICT is the premium/discount tool, which helps traders determine whether the market is currently in a premium (overvalued) or discount (undervalued) zone. This tool divides the market into two key areas:
- Premium Zone: A region where prices are expected to reverse downward.
- Discount Zone: A region where prices are expected to reverse upward.
For scalping, knowing these zones allows traders to focus on the discount areas for buying opportunities and the premium areas for shorting opportunities. When combined with other ICT indicators, this tool becomes even more powerful for executing fast, efficient trades.
Kill Zones
Kill Zones are a critical part of ICT scalping, marking the high-probability time frames where the market is most likely to see volatility and rapid price movements. These are generally during the London Open, New York Open, and other key trading session overlaps.
By trading within these time frames, scalpers can capitalize on heightened market activity, increasing their chances of success. The Kill Zones are essential in ensuring that scalpers are trading during times when liquidity is high and prices move more predictably.
Order Blocks and Liquidity Pools
Order blocks are areas in the market where institutional orders are placed. Scalpers can use these blocks to anticipate price reversals or consolidation points. By placing trades near order blocks, traders can take advantage of short-term price corrections before the market continues in its direction.
Liquidity pools act as magnets for price movement, often triggering sharp price reactions. Scalpers use these areas to make quick trades when the price hits these liquidity zones, aiming for small but consistent profits. By understanding the relationship between order blocks and liquidity pools, ICT scalpers can gain an edge in predicting short-term market behavior.
Indicators for Scalping Precision
Although the ICT strategy itself doesn’t rely heavily on traditional indicators, combining it with a few key tools can enhance your scalping accuracy:
- Moving Averages: Helps in identifying short-term trends.
- Fibonacci Retracement: Useful for identifying support and resistance levels within the premium/discount zones.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Can signal overbought or oversold conditions for confirming trade entries or exits.
Step-by-Step Guide – How to Use the ICT Scalping Strategy
Implementing the ICT Scalping Strategy requires a systematic approach to ensure high precision and profitability. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you apply this strategy effectively in your day trading routine.
Setting Up Your Chart
Start by setting up your chart with the appropriate time frames—typically 1-minute or 5-minute charts. These time frames allow you to capture rapid market movements, which are key for scalping. Use the ICT premium/discount tool to mark out premium and discount levels, as well as other ICT-specific tools like order blocks and liquidity zones.
Ensure your chart is also aligned with Kill Zones, marking the London Open, New York Open, or other session overlaps to maximize volatility. This setup will allow you to trade during times of heightened liquidity, which is crucial for scalping.
Identifying Liquidity Zones and Market Structure
Before making any trades, it’s important to identify the market structure and liquidity zones. Liquidity zones act as magnets for price movement, making them key targets for scalping trades.
Examine where large buy and sell orders are likely placed, as these zones are often areas where price reversals or sharp movements occur. Also, keep an eye on order blocks, as these institutional trading zones can signal potential reversals or consolidations—ideal for scalping.
Waiting for the Kill Zones
Timing is everything in scalping, and the Kill Zones provide the perfect windows for entering the market. These are the times when the market is most active, often during major trading sessions like the London and New York Opens.
Wait for these zones to align with your identified liquidity pools and market structure before entering trades. By trading during these times, you can capitalize on volatility and liquidity spikes, ensuring that your trades are both quick and profitable.
Executing Trades
Once all the criteria have aligned—market structure, liquidity pools, and Kill Zones—it’s time to execute the trade. For scalping, precision is key, so make sure to enter your trades at discount zones for buying opportunities and at premium zones for selling or shorting opportunities.
Always set tight stop-losses to manage risk and prevent losses from accumulating. Scalping is about making quick profits, so staying disciplined with both entries and exits is essential for success.
Risk Management
Good risk management is essential for any scalping strategy, especially when it comes to ICT. Use tight stop-losses to limit potential losses on any given trade. Given that scalping involves multiple trades in a day, small losses can quickly accumulate, so it’s crucial to control position sizes and ensure you’re not risking too much capital on a single trade.
In scalping, win rate is more important than the size of each win. As long as your trades have a high success rate, even small profits can add up to significant returns over time.
Best Times to Use ICT Scalping Strategy
One of the most important factors in the ICT Scalping Strategy is timing. Scalping requires high liquidity and fast price movements to make quick, profitable trades. The best times to use the ICT scalping strategy are during key trading sessions when the market is most active. These periods are referred to as Kill Zones, which are ideal for executing trades with higher chances of success.
Trading During Kill Zones
The ICT methodology emphasizes the importance of Kill Zones, which are specific time periods when the market experiences increased volatility. These periods are based on major forex trading sessions, particularly the London Open and New York Open. These are times when liquidity enters the market, making it more predictable and easier to scalp small price movements.
- London Kill Zone (7 AM – 10 AM GMT): The London session is one of the most active times in the forex market. Scalping during this window is advantageous because there is a high influx of market participants, creating fast and sharp price movements.
- New York Kill Zone (7 AM – 10 AM EST): Similarly, the New York session also offers a high level of market activity, especially when it overlaps with the London session. This overlap between the London and New York sessions can result in significant volatility, offering numerous opportunities for scalping trades.
Volatility Spikes Around Major News Events
Aside from trading during Kill Zones, another great time for using the ICT scalping strategy is during major news releases. News events such as central bank announcements, economic data releases, and geopolitical events can cause sudden price fluctuations, which scalpers can capitalize on. However, it’s important to stay cautious, as news-driven volatility can lead to slippage or unpredictable market behavior.
When trading around news, make sure to:
- Monitor an economic calendar for upcoming announcements.
- Trade only if the event fits within your risk tolerance.
- Have your stop-losses set tightly to avoid large losses during unpredictable price swings.
Avoiding Low Liquidity Periods
Scalping requires fast market conditions, which is why it’s crucial to avoid periods of low liquidity, such as the hours between the New York close and the Asian session open. During these times, the market tends to move more slowly, making it harder for scalpers to capture quick profits.
By focusing on high-liquidity periods like the London and New York Kill Zones, and avoiding quieter trading periods, you can increase the effectiveness of your scalping trades.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ICT Scalping Strategy
Like any trading approach, the ICT Scalping Strategy has its set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these can help traders decide whether this method aligns with their goals and risk tolerance. Below, we’ll explore the benefits and potential drawbacks of using this strategy.
Advantages of ICT Scalping Strategy
The ICT Scalping Strategy offers numerous benefits for traders looking to make quick profits in a highly volatile market. Here are some of the main advantages:
- Quick Profits: One of the biggest attractions of scalping is the ability to capture quick, small profits throughout the trading day. By taking advantage of rapid price movements in the market, scalpers can accumulate gains with multiple trades in a short period.
- Minimized Market Exposure: Because scalpers hold positions for only a few minutes at a time, they reduce their exposure to larger market risks. This minimizes the impact of unpredictable events or news that could cause major market swings, making it a safer approach for short-term traders.
- High Frequency of Trades: The ICT Scalping Strategy allows for a high frequency of trades, which means more opportunities to profit. The Kill Zones and liquidity zones within the strategy ensure that traders are operating during periods of high activity, maximizing the number of potential trades.
- Well-Defined Entry and Exit Rules: ICT focuses on precise entry and exit points, making it easier for scalpers to follow a clear set of rules. The use of premium/discount zones, liquidity pools, and Kill Zones provides clear signals for when to enter and exit trades, helping to maintain discipline.
- Suitable for All Markets: The ICT Scalping Strategy can be applied across different markets, including forex, stocks, commodities, and cryptocurrencies, making it versatile for traders who prefer to operate in multiple asset classes.
Disadvantages of ICT Scalping Strategy
While the ICT Scalping Strategy has many benefits, it also comes with some drawbacks that traders need to be aware of before adopting this approach.
- Time-Intensive: Scalping requires constant attention to the markets, as trades are executed quickly and frequently. Traders need to be available to monitor charts, identify opportunities, and manage their positions in real time. This can make scalping a highly time-consuming strategy compared to longer-term trading approaches.
- High Stress Levels: Given the fast-paced nature of scalping, it can be stressful, especially for inexperienced traders. The need to make rapid decisions under pressure, combined with the risk of small losses adding up, can lead to emotional strain and trading fatigue.
- Small Profit Margins: Since scalping involves capturing very small price movements, the profit margins for each trade are relatively low. To make the strategy worthwhile, scalpers must make multiple trades throughout the day, which can increase transaction costs due to spreads and commissions.
- High Transaction Costs: Frequent trading leads to higher transaction costs, especially in markets with wide spreads. Traders need to account for these costs when calculating their overall profitability, as they can eat into the small profits made from individual trades.
- Requires Strict Discipline: Scalping is not for the undisciplined trader. The ICT Scalping Strategy requires strict adherence to risk management rules and trading psychology. Impulsive trading or deviating from the strategy can quickly lead to losses.
Conclusion
The ICT Scalping Strategy is a powerful and precise trading method designed for short-term traders looking to profit from rapid market movements. By using tools such as premium/discount zones, Kill Zones, and liquidity pools, scalpers can make well-timed entries and exits, reducing market exposure while capturing small but frequent profits.
However, this strategy comes with its own set of challenges. It requires high discipline, focus, and a solid understanding of risk management. Traders must be prepared for the fast-paced environment of scalping, which can be both mentally taxing and time-consuming.
For those who are able to master the necessary skills and maintain strict trading discipline, the ICT Scalping Strategy can be a highly effective tool in their trading arsenal. It offers the potential for quick profits, low market exposure, and is applicable across various markets. However, it’s crucial to weigh the pros and cons and ensure it aligns with your personal trading style and risk tolerance.
In conclusion, while ICT scalping is a high-frequency strategy with promising opportunities, it demands a careful, calculated approach to be successful. As with any strategy, practice and experience are key to achieving consistent results.
Read More A Quick Guide to ICT Premium Discount
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ICT Scalping Strategy?
The ICT Scalping Strategy is a short-term trading technique developed by the Inner Circle Trader (ICT). It focuses on taking advantage of small price movements in highly liquid markets, primarily during high-volatility periods such as the London and New York Kill Zones. The strategy uses concepts like premium/discount zones, liquidity pools, and market structure to make precise trades.
Is the ICT Scalping Strategy suitable for beginners?
While the ICT Scalping Strategy can be learned by beginners, it requires a deep understanding of market structure, risk management, and the ability to make quick decisions. Beginners should first gain experience in basic trading techniques before attempting scalping, as it can be stressful and demands discipline.
What time frames are best for ICT scalping?
ICT scalpers typically use short time frames, such as the 1-minute or 5-minute charts. These time frames allow traders to quickly capture small price movements, which is essential for the scalping strategy.
What are the key tools and indicators used in ICT scalping?
Key tools for ICT scalping include the ICT Kill Zones, liquidity pools, premium/discount zones, Fibonacci retracements, and market structure analysis. These indicators help traders find optimal entry and exit points in highly volatile markets.

Hi, I’m Seojin Lee, an experienced trader focusing on the U.S. stock market, particularly NASDAQ and E-mini S&P futures. As a Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA), I apply my knowledge of financial analysis and market strategies to identify profitable opportunities.
I specialize in both short-term and long-term trading, always balancing risk management with market trends. With years of experience, I continuously refine my strategies to adapt to market shifts. If you’re interested in trading insights or strategies, you’ve come to the right place!