An ICT breaker block is a failed order block that signals a shift in market momentum. It is typically identified after a strong price movement where the market is unable to sustain its direction, resulting in a reversal pattern. This phenomenon highlights a change in market sentiment and provides traders with potential entry or exit signals, making it a valuable tool in technical analysis and smart money trading strategies.
What is an ICTBreaker Block in Forex?
An ICT breaker block, as defined by the Inner Circle Trader (ICT), is a failed order block that results in a major shift in market liquidity, which can flip the market structure from bullish to bearish or vice versa. When an order block fails, it alters the current market outlook and acts as a key indicator for future market movement.
The core idea behind these blocks is the search for liquidity by market algorithms. Traders typically spot these order blocks to forecast market movements. A bullish breaker block is expected to drive prices up, while a bearish breaker block should have the opposite effect. As a result, traders position their stop losses below the level for bullish scenarios and above it for bearish ones.
However, market makers and smart money traders often take advantage of these situations, triggering stop losses and pushing the market in the opposite direction by creating a liquidity grab. This is where the concept of breaker blocks becomes highly relevant.
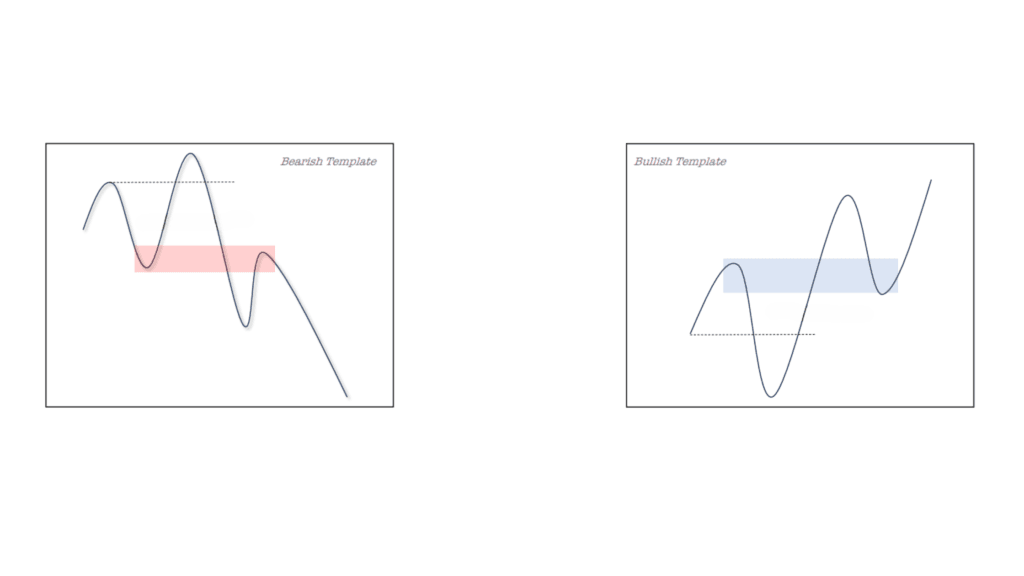
Difference Between Breaker Block and Order Block:
| Concept | Order Block | Breaker Block |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Last up/down candle before a big move (used for entries) | A failed order block that becomes a new resistance or support |
| Market Behavior | Price returns to it and respects it | Price breaks it, then uses it as support/resistance on the other side |
| Signal | Continuation of trend | Reversal of trend |
How To Find An ICT Breaker Block?
When identified as a failed order block, a breaker block (BB) takes on a new role: it becomes a level of support or resistance. This shift is critical in understanding how to use BB in forex trading. A failed bullish order block transforms into a bearish breaker block, and a failed bearish order block turns into a bullish breaker block. This role reversal is central to leveraging breaker blocks for predictions and strategy formulation.
Unlike order blocks, where traders focus on the price level where institutional traders make large buys or sells, a breaker block represents the end of smart money pressure. A prime example is George Soros’ famous trade in 1992, where he made a $1 billion profit by betting against the British Pound, a classic instance of a breaker block.
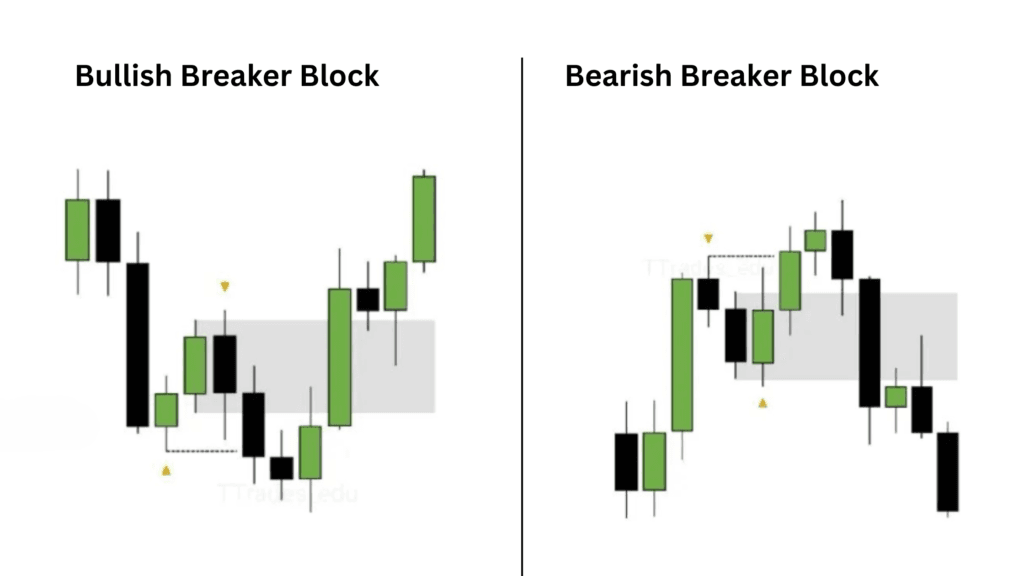
What is ICT Bullish Breaker Block
When an ICT bearish order block fails, it can transform into a bullish ICT breaker block. In future price action, when the price revisits this area, it tends to act as a support zone. This is because the failed bearish order block—now a bullish breaker block—provides a level where buyers are expected to step in, potentially pushing the price higher as they defend the area from further downside movement.
What is ICT Bearish Breaker Block
A bearish breaker block occurs when a previous bullish order block fails, and price breaks through it, signaling a shift in market sentiment from bullish to bearish. Once the bullish order block is breached, it transforms into a bearish breaker block, which now acts as a resistance zone in future price action.
When price revisits this area, the former bullish breaker block often functions as a resistance level, where sellers may enter the market, pushing the price lower. Traders look for bearish reversal signals in this zone, as it typically marks an area where selling pressure could dominate, leading to further downward movement.
How to Use Breaker Blocks in Forex Trading?
Using breaker blocks effectively in trading can be a bit challenging. To use them to your advantage, here’s a step-by-step guide:
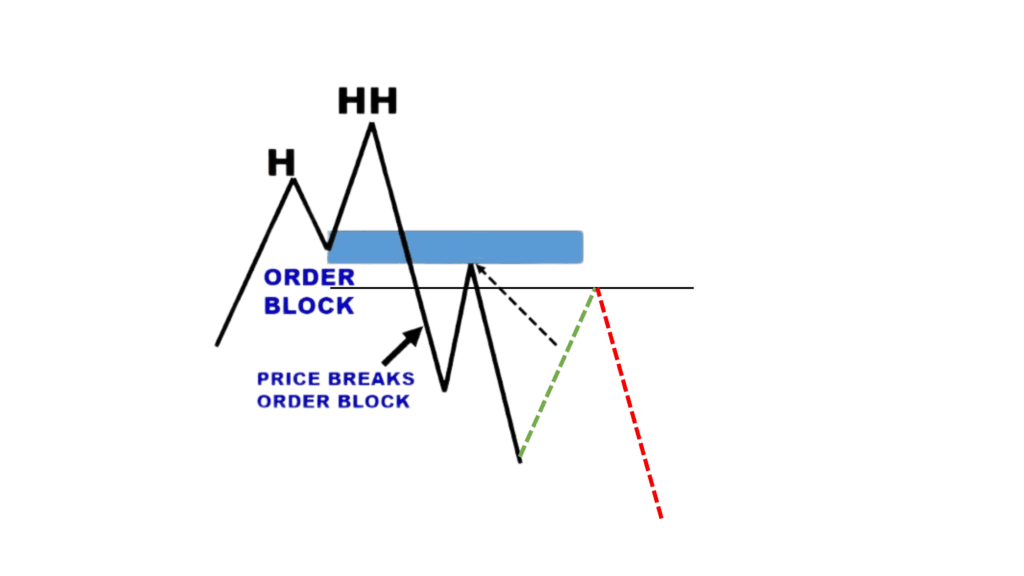
- Identify a Market Structure Shift
The first step is recognizing when the market structure shifts. By analyzing price movements, you can determine if the market has broken its previous order flow and reversed direction. Identifying this shift is key to spotting potential breaker blocks. - Identify the Breaker Block
A breaker block is a failed order block that signals a change in momentum. It is typically identified after a significant price movement where the market fails to sustain its direction and reverses. Once the trend changes, the failed order block takes on an opposite role, just like support levels become resistance after a price breach. For example, failed bullish order blocks become bearish breaker blocks, and failed bearish order blocks become bullish breakers. - Expect Price to Return to the Breaker Block
Once a breaker block is identified, traders expect the price to return to this level. This retest often signifies a consolidation phase before the market decides its next move. - Wait for Confirmation and Enter a Position
Before entering a trade, wait for confirmation at the breaker block level. This confirmation may come in various forms, such as the formation of fair value gaps as shown below image.
How to Trade Using the Breaker Block Strategy?
Trading with the breaker block strategy is straightforward. Here’s how to apply it to the GOLDUSD chart on the 15-minute timeframe:
Identify Large Order Blocks: Look for areas on the price chart where significant order blocks are present. These are often areas of concentrated buying or selling activity by institutional traders.
Spot a Market Structure Shift: In the XAUUSD chart, you can observe a shift in market structure. Initially, the price was making higher highs and higher lows, indicating an uptrend. However, the price then broke below a higher low and formed a lower low, signaling a potential trend change. This is a signal to start looking for sell opportunities.
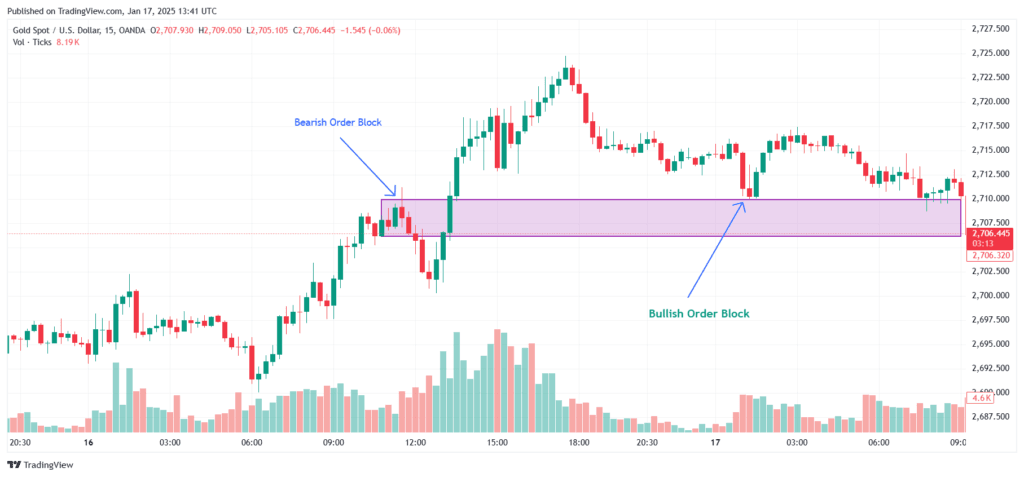
Look for a Failed Order Block: After the market structure change, a failed bearish order block transforms into a bullish breaker block. Traders anticipate that the price will return to this level. The expectation is that the breaker block will act as support, and when the price reaches this level, a reversal may occur.
Wait for Confirmation at the Breaker Block: Once the price returns to the breaker block, do not enter immediately. Wait for a bearish candlestick pattern to form as confirmation of a downward move before entering a sell trade.
Implement Risk Management: To manage risk effectively, aim for a minimum of three risk-reward profit targets. For stop-loss placement, set your stop loss above the candlestick formation if you are entering a sell position. Conversely, for a buy position, place your stop loss below the candlestick pattern to protect against adverse price movements.
Which timeframe is best for finding the Breaker block?
From a trade execution point of view, combining ICT (Inner Circle Trader) concepts like Market Structure Shift (MSS), Fair Value Gaps (FVG), and trading during the kill zones on shorter timeframes like the 15-minute (15M) and 5-minute (5M) charts can be highly effective for precise entries.
What is the win rate of the breaker block trading strategy?
The win rate for this strategy is approximately 77%, as confirmed through backtesting. However, its effectiveness largely depends on the trader’s understanding of market volatility and overall market conditions.
How can I use ICT Breaker Blocks to predict market reversals?
ICT Breaker Blocks help predict market reversals by identifying a key candle that was once support or resistance but got broken and then acts as a reversal zone. To use them, first look for a strong move in price followed by a break of a previous swing high or low. The candle just before that break becomes the breaker block. When price comes back to this zone, it often reverses. So, you watch for price to return to the breaker block and show rejection—this is where you can enter a trade, expecting the market to reverse from that area.